Cloud Infrastructure: What Is It and How It Can Benefit Your Business

For many businesses, one of the worst scenarios is losing their data, having sensitive information, experiencing hardware failure, or being attacked by ransomware. Without the necessary security measures and proper cloud infrastructure, businesses need to face the reality that they could lose millions.
In today’s competitive and digital world, your business operations' safety, scalability, and efficiency must be protected. Cloud infrastructure provides the backbone that protects your data and enables your business to grow, adapt, and thrive in a rapidly changing environment.
There’s no need to worry, however, by understanding cloud infrastructure, what it is, and how it can benefit your business, your company and employees can work more efficiently and securely.
This article will give you all the information you need about cloud infrastructure, and what options you have available to reduce the threat of data loss, cyberattacks, and other threats to data.
Table of contents
- Cloud infrastructure vs cloud architecture
- Advantages of cloud infrastructure
- Cloud infrastructure tools
What is cloud infrastructure?
Cloud infrastructure is a collection of hardware and software that make up the cloud. These resources include servers, storage, networking hardware, and virtualization software, which work together to deliver computing power and services over the Internet.
The four elements that make up cloud infrastructure include:
- Servers: The servers are computers which a cloud provider installs across data centres, and are powered by processor cores and memory storage. The providers use groups of interconnected servers to provide different cloud computing services.
- Storage: This is data hosted on a physical architecture, and you can access cloud storage from any device connected to the Internet.
- Networking: ensures that the cloud infrastructure is connected to data different data storage, applications, microservices etc, to communicate between resources and users worldwide.
- Virtualization: this software allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server to maximize efficiency.
Businesses that need cloud storage for large amounts of data can lease a cloud infrastructure or buy from a cloud storage reseller to avoid the costs and maintenance of on-premise storage and instead opt for a pay-as-you-go service, such as object storage.
Different types of cloud infrastructure
A cloud infrastructure model is used in the three main cloud computing models: public, private, and hybrid. An organization will pick from one of these based on their needs.
Public
A public cloud model is a third-party provider that owns and manages the cloud infrastructure and is shared with multiple customers. These customers rent the CPU, storage, and bandwidth, and only pay for what they use.

Customers do not own or maintain the hardware - this is done by a third party. A Public cloud infrastructure offers services on demand and is popular for its flexible pricing, pay-per-use, or long-term contracts.
Private
Unlike public cloud storage, an organization has a dedicated cloud infrastructure hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. It gives users exclusive access to computing resources so they have full control over the cloud infrastructure, including managing and maintaining the hardware or software.
Larger businesses will choose a private cloud infrastructure for its security, privacy, and customization benefits. However, a private cloud infrastructure for its security, privacy, and customization benefits. However, a private cloud model is more expensive, difficult to maintain, and less scalable than other models.
Hybrid
A hybrid cloud model combines private and public clouds to keep sensitive data and critical workloads in the private cloud and less-sensitive data in the public infrastructure. This model is popular for businesses that want full privacy but also scalability to meet their storage needs.
What are the different cloud computing models?
Each cloud computing model offers users different levels of control, flexibility, and management. Below are the most common models.
Software as a service
Software as a service (SaaS) is an application provided by a host who manages and hosts the cloud platform, such as Internxt Drive. Users log in to the service via a browser or application without the need to install or maintain the service.
With a SaaS model, the provider handles the infrastructure, maintenance, and updates.
Platform as a service
Developers usa a PaaS platform to build, test, and deploy apps without managing the underlying infrastructure, helping them streamline the app development and deployment process.
PaaS provides the necessary development tools, databases, and other business resources so developers can focus on the code and app functionality.
Infrastructure as a service
An IaaS model provides organizations access to virtual computer resources, such as servers, storage, and networking over the internet. Users usually pay rental or pay-as-you-go costs, and they maintain control over the infrastructure, operating systems, and storage.
In this case, the provider takes care of hardware maintenance.
Function as a service
FaaS is a cloud and serverless computing model for developers to run individual functions of code snippers to respond to events without managing the underlying cloud infrastructure.
FaaS automatically scales based on demand, so developers focus on writing code rather than server management.
Cloud infrastructure vs. cloud architecture
Cloud architecture focuses on the design and operational strategies, whereas cloud infrastructure ensures the physical capabilities that make this possible.
Cloud architecture is the design and organization of the components and services that build the cloud environment. A cloud provider uses availability zones (AZs), which are multiple interconnected physical data centers, to provide its services.

Cloud architecture defines how a cloud provider's services interact and the strategies needed to provide scalability, performance, reliability, and security.
Cloud Infrastructure represents the cloud architecture plans, with a physical representation of the hardware, operating systems, and resources to deliver cloud services. A public cloud infrastructure will provide the capabilities of these resources to provide them as services for its customers.
Advantages of cloud infrastructure
Cloud infrastructure offers many benefits for individuals, businesses, and large-scale enterprises to handle data securely and safely while keeping costs at a minimum.
Scalability
With different cloud storage models available, businesses can pick and choose their provider, and opt for a storage plan that suits them. Different kinds of storage plans may have fixed storage amounts, or you can pay and upgrade your storage with object storage plans, to upgrade storage when needed and only pay for the storage you use.
Cost-effectiveness
A cloud infrastructure eliminates the need for physical hardware and reduces maintenance costs, lowering overall IT expenses and reducing the chances of hardware failure or security vulnerabilities.
Accessibility
One of the benefits of a cloud infrastructure is its flexibility, allowing users to access their files from any device or operating system. Aside from offering apps for Windows, Mac, and Linux, companies like Internxt also offer WebDAV, Rclone support, and S3 storage to offer cloud infrastructure that meets the needs of anyone.
Disaster recovery
Cloud infrastructure often includes built-in redundancy and backup solutions to improve data protection and recovery capabilities. Backups allow data to be restored in case of disaster, so should a server shut down the files can still be accessed and restored from another server thanks to data redundancy.
Automatic updates
Cloud infrastructure is typically updated by the cloud provider to improve performance and to prevent cyberattacks, which is crucial to prevent data breaches. Regular updates reduce the burden on IT teams, and customers can use the best version of the service without worrying about advanced issues.
Enhanced security
Security is crucial when dealing with any service online, and the best cloud infrastructure models will include AES-256 encryption to protect files during transit and stored in the cloud. Additional security measures like firewall protection will help businesses meet security audits and compliance regulations.
Resource management
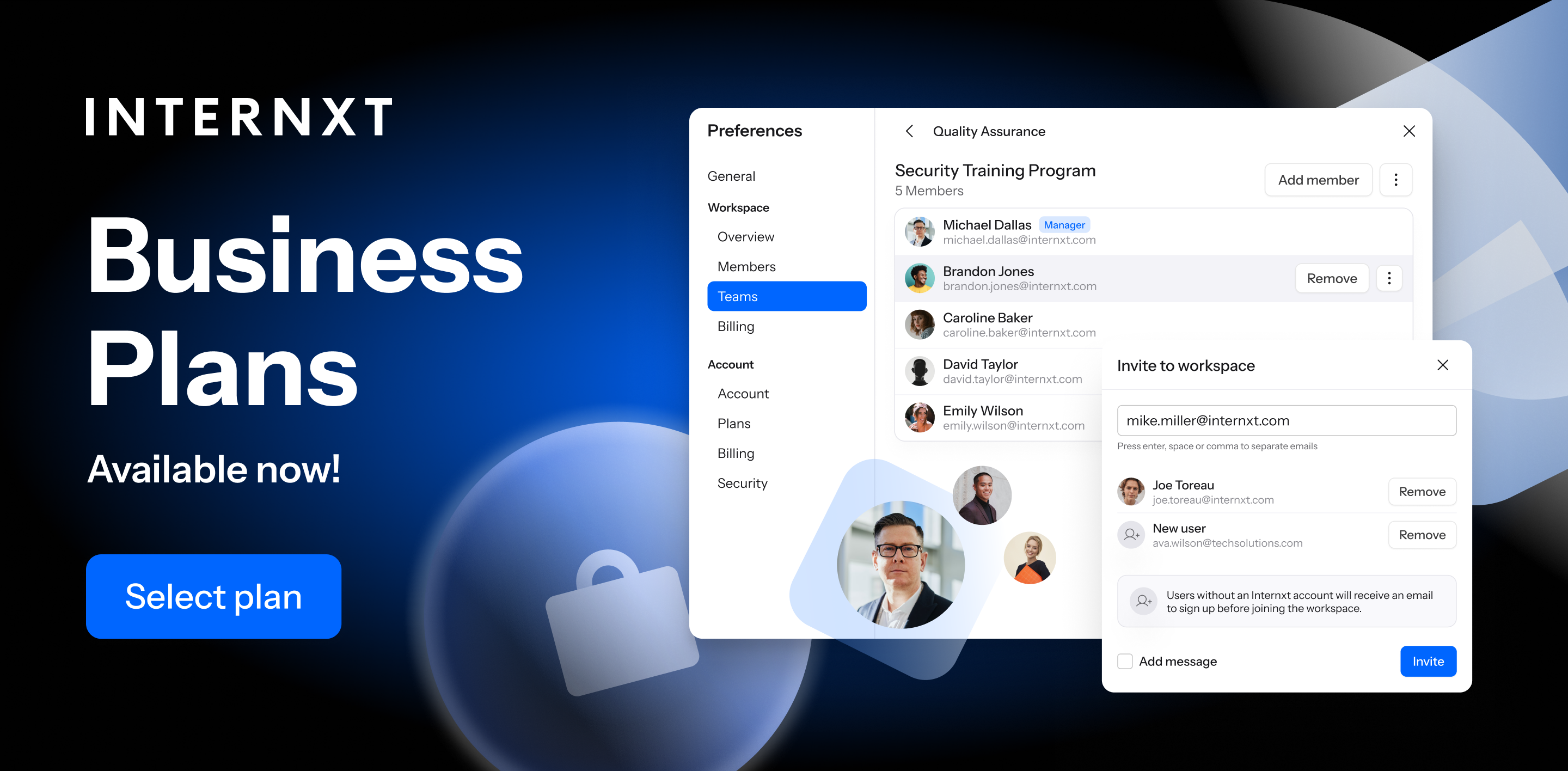
Cloud infrastructure provides businesses with efficient resource allocation and utilization, optimizing performance, reducing costs, and automate process in the cloud. For example, with Internxt business plans, account managers can allocate storage for up to 100 users and pay on a per-user basis.
Cloud infrastructure tools
Here are some different cloud infrastructure tools your business can use to easily migrate to the cloud.
Internxt
Internxt Drive is a SaaS public cloud storage provider offering individual, business, and object storage plans emphasizing security and privacy and complying with the complying with the GDPR.
Internxt's encryption differs from that of other cloud providers. It doesn’t control the encryption keys on the servers; instead, only the user can access these keys, so nobody can view, monitor, or access files.
This encryption offers users much more privacy from companies such as Google, who are notorious for privacy violations. As they hold encryption keys to your data, they could decrypt and access these files if required by law.
To learn more about Internxt's infrastructure, you can get more information about our data centres from our website.
Heroku
Heroku is a platform and service model that enables developers to build, run, and operate applications entirely in the cloud.
Heroku supports various programming languages, including Ruby, Node.js, Python, and Java, allowing developers to use their preferred tools. The platform offers a rich ecosystem of add-ons, providing functionalities such as databases, caching, and monitoring services, which can be easily integrated into applications.

Heroku's deployment process is streamlined, allowing developers to push code updates with a simple command. Additionally, it automatically handles scaling, meaning applications can grow as needed without manual intervention.
Terraform
Terraform is an infrastructure as a service (IaaS) tool for developers to create, manage, and version infrastructure consistently across multiple cloud providers and on-premises environments.
With Terraform, users can automate the setup of complex environments, ensuring that infrastructure is reproducible and predictable. The cloud infrastructure tool uses a declarative approach, meaning users define the desired state of the infrastructure, and Terraform takes care of the underlying changes needed to achieve that state.
Terraform also promotes team collaboration by allowing infrastructure changes to be versioned and reviewed in a way that is similar to the application code. This makes it a valuable tool for organizations looking to streamline infrastructure management and improve operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Start your business journey with cloud infrastructure and integrate the tools to set up your business for success. Be sure to keep up to date with Internxt and subscribe to any of our cloud storage plans to help keep you secure online!

