Object Storage vs. File Storage vs. Block Storage - What's Best for Businesses?

For businesses, choosing the right cloud storage becomes more complex than for the average user because factors other than personal preferences and needs come into play. Companies need to consider the big picture when choosing a storage solution for their data.
Businesses often deal with sensitive data, large files, and complex storage needs. Data security compliance regulations scalability, and integration with existing systems become crucial considerations if businesses want to protect their reputations and finances and prevent data breaches.
Additionally, businesses may need to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of cloud storage, considering storage capacity, bandwidth, and additional features. These complexities highlight the importance of careful evaluation and selection for businesses seeking a cloud storage solution that meets their requirements.
Businesses will often need to consider object storage vs. block storage vs. file storage, as these meet their needs to store huge data lakes in a manageable, scalable, and cost-effective way.
Therefore, we will examine the differences between object, block, and file storage and consider the pros and cons of each to help your business migrate to the cloud and make the best decision to protect company and customer information.
Table of contents
- Pros and cons of file storage
- Use cases of file storage
- File storage example: Internxt Drive for Business and Families
- Object storage vs file storage vs file storage differences
- Object storage vs file storage vs block storage conclusion
What is object storage?
Cloud object storage is a kind of cloud storage that divides data into separate, self-contained units called objects. Unlike file storage, these objects are stored in a flat structure and not in folders or sub-directories, and the data is not stored in one single file.
Each object has a unique identifier that can be used to access it, and each object includes metadata attached to it that helps with better processing and usability. Users can set the value for fixed-key metadata or create custom metadata.
You may also see the terms cold and hot cloud storage, this simply means that hot storage is meant for rapid data access. Cold storage is for files that don't need to be accessed as quickly, which sometimes can be cheaper, but not always.
Finally, object storage allows you to store objects locally or in the cloud, but you must use an API to access and manage them. For this, you will need S3-compatible object storage.
S3-compatible object storage is a type of cloud storage that aligns with the Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) API. This means it offers features, functionality, and interface similar to S3, making migrating applications and data between providers easy.
Because of these features, you can connect your object storage to Rclone, Cybrduck, and more, giving you a versatile and new way to manage your storage.
Object storage example: Internxt Drive
Internxt offers S3-compatible object storage for businesses at an 80% more affordable cost than AWS, Azure, and Amazon because there are no additional charges for data transfer.

Get started with Internxt S3 for €7 per TB. Pay only for the storage you use, and scale it to meet your business storage needs.
Pros and cons of object storage
As businesses face the challenge of storing huge amounts of data, many choose efficient object storage products for better scalability, security, and usability. Here’s why.
Pros
- Efficient for large unstructured data: Ideal for managing massive amounts of unstructured data, which is crucial for AI, machine learning, and big data analytics.
- Pay-as-you-go model: You only pay for the storage you use, making it more cost effective than traditional file storage, which often requires upfront payment for a fixed amount.
- Unlimited scalability: Object storage can grow with your needs, allowing you to store petabytes or more as required.
- Metadata integration: Each object stores its metadata, making retrieving and extracting valuable insights from your data easier.
- Enhanced search capabilities: Advanced search features allow you to search metadata and object contents to quickly access specific data.
Cons
- Slower performance for frequent updates: Object storage needs to be optimized for rapid data changes, making it less suitable for workloads that require frequent updates.
- Complexity for transactional data: It’s not ideal for handling transactional data where consistency and real-time access are crucial.
- Limited compatibility with legacy systems: Older applications may not natively support object storage, requiring additional integration efforts.
- Higher retrieval latency: Retrieving data from object storage can be slower than retrieving data from other storage types, especially for small, frequent requests.
Use cases for object storage
Object storage is commonly used in these scenarios due to its scalability, affordability, and ability to store vast data sets.
- Backup and archiving: Its scalability and cost-effectiveness make it a great choice for long-term data storage, backups, and archival needs.
- Media and content storage: This is perfect for storing and sharing files like images, videos, and audio, with metadata support for easy retrieval.
- Cloud-native applications: Many modern cloud applications rely on object storage for its scalability, flexibility, and ability to handle large datasets.
- Disaster recovery: Object storage is commonly used for disaster recovery plans, providing affordable off-site data storage that businesses can scale when necessary.
What is file storage?
File storage saves all data in a single file type determined by the application used to create the file/type, e.g., .jpg, .docx, or .txt.

File storage saves and manages documents to your computer's hard drive or a company’s network. It can also be done using devices like Network-Attached Storage (NAS), cloud storage, network drives, or flash drives.
File storage uses a simple, hierarchical system where files are organized into folders and subfolders, making them easy to find and manage. File storage is a suitable option for small to medium-sized businesses, departments, or individuals.
Pros and cons of file storage
File storage is the most common kind of storage, and most people using online storage use it for presentations, reports, spreadsheets, graphics, photos, etc. The pros of file storage are:
Pros
- Easy to access on a small scale: Users can quickly find, open, and save files with just a few clicks, especially when dealing with a moderate number of files.
- Familiar to most users: It’s the most common storage system, so people with basic computer skills can easily navigate and manage their files without extra cybersecurity training.
- User control over file management: End users can create, move, and delete files using a simple interface, giving them direct control over their data.
- Customizable access rights: Administrators can set files as read-only, writable, or locked and even password-protect them, offering flexible control over file access.
Cons
- Difficult to manage at large scales: As the number of folders and files grows, navigating and organizing them becomes time-consuming, and search times increase, leading to inefficiency across an organization.
- Not ideal for unstructured data: While file storage can handle unstructured data like text or sensor data, it’s not the best option, especially for managing large volumes.
- Costly at large scales: As storage capacity is reached, additional hardware needs to be purchased, making scaling up expensive.
Use cases of file storage
Due to the popularity, ease of use, and familiarity of file storage, it can be used for the following cases:
- Personal data management: Ideal for individuals organizing documents, photos, and videos on their computers or personal cloud storage.
- Small to medium-sized businesses: Suitable for companies with a manageable number of files and folders, where straightforward file organization is needed.
- Collaborative work environments: Effective for teams that need to share and access common documents, spreadsheets, and media files.
- Departmental file storage: Useful for departments with structured data and standard file types, where users can easily create, manage, and access files.
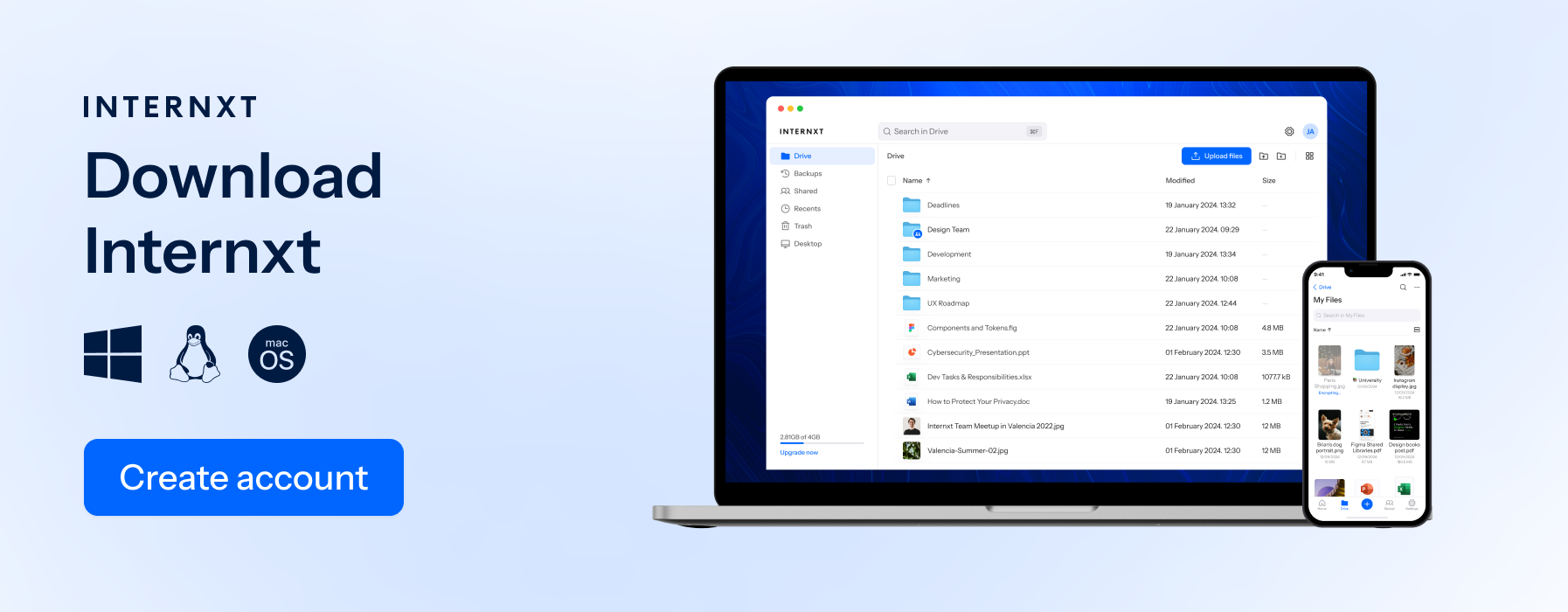
File storage example: Internxt Drive for Business and Families
Internxt Drive offers secure, businesses private cloud storage for individuals, businesses, families, and is an easy-to-use platform for sharing and organizing files.
Internxt uses end-to-end encryption and zero-knowledge policies for increased privacy, so your files are secure against hackers and data breaches. Teams and departments can she files and get access controls, which can limit access, set passwords for files, and add new members to the plan as and when required.
Internxt offers affordable and scalable plans for businesses with up to 100 users, making it the perfect solution if you need a secure and green cloud computing platform to manage your files without the huge amounts of storage required in object storage.
What is block storage?
Block Storage involves splitting data into fixed-size blocks, each with a unique identifier. These blocks can be stored separately and in different environments (e.g., one block on Windows, another on Linux). When needed, the storage system reassembles these blocks into a single file.
Block storage is commonly used for hard disk drives and frequently changing data. It can be managed on Storage Area Networks (SANs) or in cloud storage environments.
Pros and cons of block storage
Despite being the go-to storage system for tech industries over the years, many organizations are transitioning to other storage methods due to their limited scalability and lack of metadata. This makes it challenging to efficiently manage, search, and organize large volumes of data.
Even so, block storage does have some pros.
Pros
- Fast Performance: When blocks are stored locally or nearby, block storage offers high-speed access and low latency, making it ideal for business-critical applications.
- Reliable: Since each block is a self-contained unit, block storage has a low failure rate, enhancing overall data reliability.
- Easy to Modify: Updating a block is straightforward; you simply create a new version without replacing the entire block.
Cons
- Lack of Metadata: Block storage doesn’t include metadata, making it less effective for managing and organizing unstructured data.
- Not Searchable: With limited search capabilities, finding specific data in large volumes can become challenging and inefficient.
- High Cost: Expanding block storage can be expensive, making it cost-prohibitive for large-scale data needs.
Use cases for block storage
Although not the most popular decision when considering object vs. file. vs. block storage, there are some uses for it, which are:
- Databases: Ideal for transactional databases due to their high performance and ease of updates.
- Email Servers: Commonly used for storing emails because of its reliability and speed.
- Virtual Machine File Systems (VMFS): Used for deploying and managing virtual machines. Block storage allows for creating VMFS volumes that physical servers can attach to, enabling efficient management and sharing of virtual machines and files.
Object storage vs file storage vs block storage differences
As a general overview, object storage uses a distributed cloud storage environment across multiple storage nodes or servers stored as individual objects with unique identifiers and metadata. Object storage is more scalable and suitable for unstructured data lakes.
File storage organizes data in a hierarchical system of folders and subfolders and uses network-attached storage (NAS) in an on-premises setup. This makes it easy to manage for personal and small business use. One downside of file storage is it could be more efficient for large volumes and unstructured data.
Finally, block storage divides data into fixed-size blocks with unique addresses, offering high performance and reliability, especially for databases and virtual machines, but lacks metadata and can be expensive to scale.
Object storage vs file storage vs block storage conclusion
Now that you have an overview of object storage vs. file storage vs. block storage, which one is best for you? Each one has its uses depending on your business needs, size, and budget and are summarized below.
As a tool for large businesses, object storage is the way to go as it offers and affordable solution with unlimited storage options, as you only pay for each terabyte you need. For object storage, you can sign up for Internxt S3 and pay just €7 a month for each terabyte you use.
On the other hand, smaller businesses or teams will be more suited to an Internxt business plan. This is the best storage solution if you don’t have huge amounts of data but want to keep confidential information encrypted and private.
Internxt offers 2TB/user for up to 100 users, with monthly and annual plans available.
For databases and virtual machines, you can consider block storage, but be aware that this can be costly and lacks metadata, so retrieving this data will be more difficult.
For more options for object storage, IDrive also has an e2 object storage solution, which you can learn more about in our article about IDrive, and alternatives to IDrive.
Remember to consider how each storage option protects and secures your files, as businesses risk losing personal information and millions if files are not stored securely. For guaranteed private storage, choose either Internxt S3, or Internxt Drive, for peace of mind, and the best secure cloud storage.

