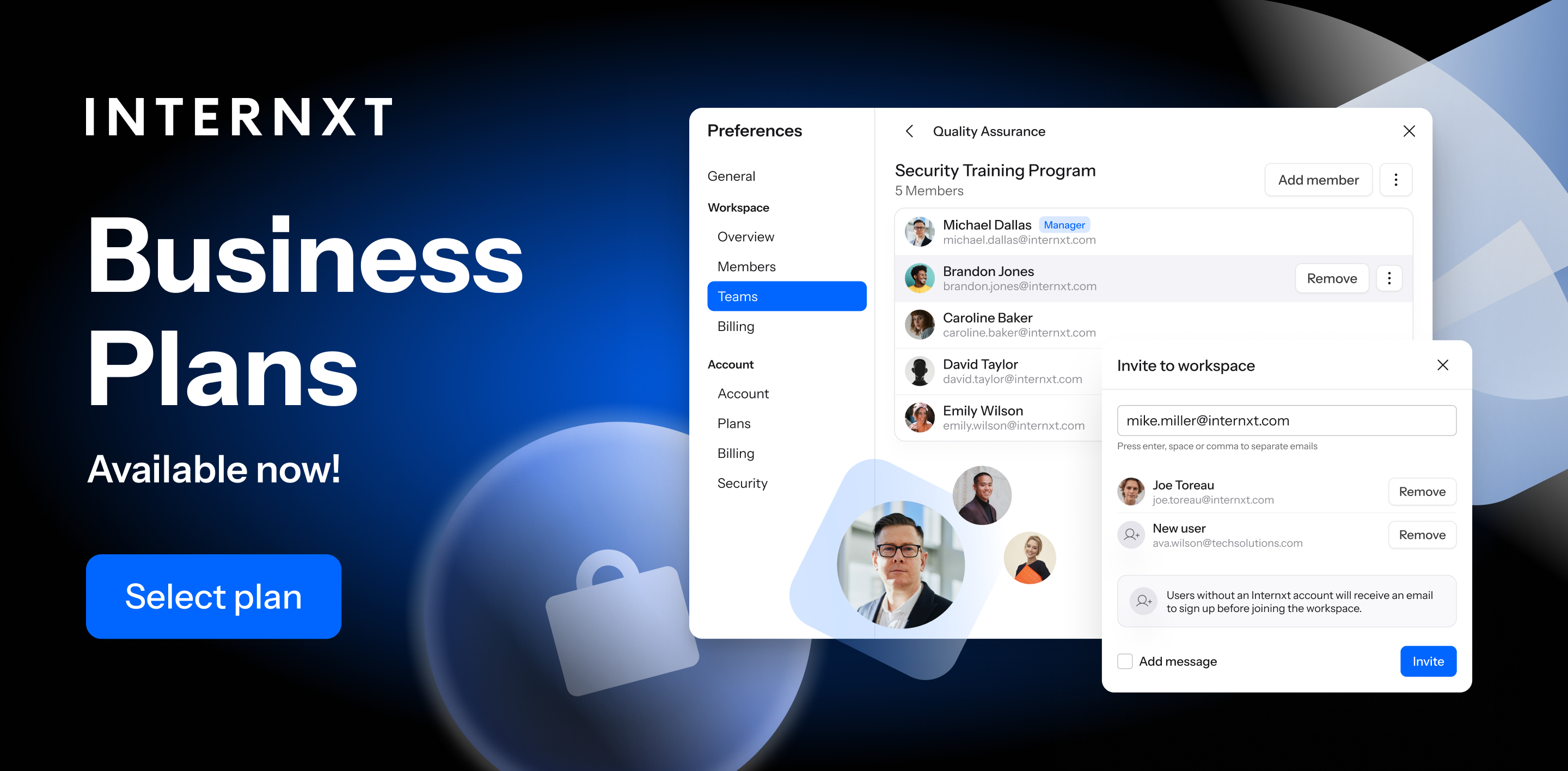
A Comprehensive Guide to Endpoint Backup and its Benefits

No matter what device you’re using, be it desktop, mobile, or tablet, all the data you store there is at risk of data loss. You could face data loss or cyberattacks such as ransomware unless you protect these files.
Securing these devices with endpoint backup and data recovery is essential for businesses and teams to protect against breaches, data loss, and other threats that can disrupt operations. For this reason, we will offer you a comprehensive guide on endpoint backup, including what it is, how it works, and more throughout this article.
So, if you’re looking for secure technologies to protect your business, find out how endpoint backups can help you and your organization.
Table of contents
- How does endpoint backup work?
- Different endpoint backup processes
- Benefits of endpoint backup
- Endpoint vs. cloud backup
- Endpoint security requirements
- Different types of endpoint backup
Endpoint backup explained
Endpoint backup is the process of creating copies of data on laptops, desktops, mobile devices, or tablets known as endpoints and securely storing them either in the cloud or on an external storage device.
Some of the most used endpoints are:
- Internet of Things (IoT) Devices
- Desktops
- Servers
- Smartwatches
- Printers
- Tablets
- Medical devices
- Point-of-sale (POS) systems
- Workstations
Endpoint backups are growing in popularity and importance due to the security and assurance that copies of data are managed and accessible in case of accidental deletion or other methods.
For organizations, the demand for backing up across all endpoints (devices) is increasing due to the popularity of remote work and the growing need for businesses to show compliance that they take measures to securely protect financial data, sensitive information, and ensure business continuity.
How does endpoint backup work?
Endpoint backups continuously or periodically copy data from the endpoints to a secure cloud storage provider or physical device. Here is an overview of the endpoint backup process.
- Backup software is installed on the endpoint device. The software monitors the files and regularly backs up data.
- The software then encrypts the data before transfer, securing it against unauthorized access during transit and storage.
- The user schedules or automatic backups or runs real-time or continuous backups.
- Encrypted data is sent to the chosen location for storage, and some backup solutions also offer backups on network-attached storage (NAS) systems.
- Some cloud providers use redundancy for extra security. Redundancy means multiple copies of data are stored across different servers, so they are still accessible should anything happen to one data center (natural disaster, server outages, etc.).
- Endpoint backup solutions may also include file versioning, allowing you to back up different files and restore earlier versions in case data is accidentally overwritten.
Each process ensures complete control and security of your files, keeping you in complete control of your data.
Different endpoint backup processes
Not all backups are the same, so you will need to set up your backup schedule and type based on your business needs. Endpoint backup typically uses the following backup solutions:
- Incremental: Incremental backups only transfer changes to the backup repository from the last changes made to minimize bandwidth usage and storage requirements.
- Differential: Differential backups only back up the data that has changed since the last full backup. If you did a full backup on Monday, a backup the next day would include all changes made since the last backup. A backup the day after would again include all changes made since Monday.
- Full backup: A full backup is a periodic backup of all selected data to a specific location for a more comprehensive approach to data protection. However, this can consume more storage space and resources, so may not be efficient for all use cases.

Benefits of endpoint backup
Endpoint backup offers many solutions to defend against data loss caused by network attacks, hackers, and other security threats. Here are some common threats or problems businesses may face and how endpoint backup limits the dangers.
- Hardware failure: Backups can be configured and transferred to new devices to keep data intact should another device fail.
- Ransomware: Ransomware is the most common attack businesses face, and with endpoint backup, you can recover any backed-up data lost to this attack.
- Human error: If an employee mishandles, deletes, or loses data, it can be recovered from a previous backup, restoring the overwritten or lost file.
- Mobile device protection: Endpoint backups are increasingly popular as technology evolves, and digital nomads use these endpoints for their business data. Therefore, mobile endpoint protection helps restore data on a new endpoint in case anything happens to the current one.
- Business continuity: Finally, an endpoint backup solution keeps files easily recoverable so businesses can maintain and run operations securely.
Endpoint vs. cloud backup
As the name suggests, endpoint backup is a device-centric approach to protecting data on individual devices. Cloud backup is a more comprehensive approach and is used to backup entire systems and provide access to data from anywhere.
In many cases, endpoint and backup complement each other as part of a layered data protection strategy; choosing the best will depend on your needs.
Endpoint backup is a popular solution for remote workers. Businesses must rely on workers to protect their devices so data is protected no matter where an employee works. This approach focuses on protecting specific endpoints rather than an entire IT system.
Cloud backup backs up data from multiple servers, networks, or cloud-based applications. By storing data off-site so it can be restored if needed, cloud backup offers businesses disaster recovery, scalability, protection against ransomware, and global accessibility.
Cloud backup also supports businesses with compliance and regulations while offering a cost-effective and scalable solution to store large volumes of data across their infrastructure rather than individual endpoints.
Endpoint security requirements
Endpoint security is often required for compliance and auditing purposes, particularly for businesses handling sensitive data or industries subject to regulatory requirements, such as healthcare and finance.
Endpoint security helps maintain data integrity, confidentiality, and availability, key components of many compliance frameworks. An endpoint security checklist helps businesses document their security for audits and demonstrate compliance.
Here are some security features to consider.
- Device security: To protect your endpoints efficiently, update the software when new releases are available, enable firewalls, and install antivirus and anti-malware programs.
- Authenticate users: The zero-trust concept helps businesses ensure access is restricted to authorized users only, reducing the risk of data leaks. To do so, enable Multi-Factor Authentication and set up automatic lockouts for accounts after a period of inactivity, so access to them requires continuous verification.
- Threat detection and response: Set up endpoint detection response software that detects and notifies your team of potential attacks and blocks unauthorized access to accounts. Use these response systems and set up a security response plan to limit damage to potential data threats.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM): MDM monitors endpoint security to protect devices if they are stolen, lost, or damaged. It can help track devices and use a remote wipe to erase data on stolen devices.
- Compliance and auditing: Ensure endpoints meet relevant regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, depending on your location. Continuously monitor the logs and devices to detect suspicious activity in these accounts and set up notifications to alert your team of any suspicious activity.
These guidelines will help set the security features for your endpoint backup solution to protect crucial data and limit the chances of cyberattacks.
Different types of endpoint backup
Different endpoint backups vary between organizations and their uses, so only some endpoints will get the same type of backup. In general, here are some of the different types and their uses.
- File-level backup: In file-level backup, all individual files and folders are backed up. This option is ideal for protecting information stored on servers and ensuring that files are still accessible even if one server is down.
- Block-Level Backup: This backup only backs up changes made to blocks of data and not entire files, a more efficient endpoint backup for large datasets.
- Database Backup: This targets all data within a system, including the structure, procedures, and transaction logs.
Whatever your business needs, there is likely an endpoint backup solution your team can use to their advantage when handling data.
How to backup your business data
There are many options for endpoint backup on the market, which your team can investigate and see if they offer the right solutions for your business. Popular examples are IDrive and Microsoft Azure, but we would like to offer another cheaper, more affordable cloud competitor with unlimited storage and backup options.
Internxt Object Storage
Internxt Object Storage is a storage solution for enterprises that need large-scale storage solutions with backup integration to protect your files from ransomware, data loss, and more.
Internxt’s Object Storage offers world-class security thanks to server-side encryption, Multi-Factor Authentication, and Identity Access Management tools. This dedication to privacy will also help demonstrate your business is compliant with GDPR for correctly and securely handling data.

Finally, compared to other endpoint backup solutions, Internxt is up to 80% cheaper than other hyper scalers, such as Microsoft, Amazon, and Google, thanks to its pay-as-you-go model of €7 per TB per month, which you can scale to your storage needs.
With no data transfer fees, Internxt is the best option for your business to store as much data as you need at an affordable cost.
Conclusion
Businesses can’t afford to ignore endpoint backup protection in their cybersecurity plans. Without it, they could face millions in losses from data breaches or cyberattacks.
For all your storage needs and data security, consider Internxt encrypted cloud storage, your new cloud storage for business that protects and backs up whatever you need.

