Data Breaches of 2023 that Left Healthcare Industries in Critical Condition

The EU Healthcare system is under attack. Between January 2021 and March 2023, the health sector faced various cybersecurity incidents, endangering the confidential information of hospital and patient data.
For the 13th year in a row, the healthcare industry reported the most expensive data breaches, averaging a cost of USD 10.93 million. This year, 40 million patients have already been impacted by data breaches, indicating that 2023 is on track to set a new record for attacks on the health sector.
Report of Data Breaches in Healthcare in 2023
The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) conducted a report documenting all cybersecurity incidents reported at the start of 2023. Of these incidents, 53% were aimed at healthcare providers, with hospitals being the main target of attacks.
The Most Common Cyberattack to the Healthcare Industry
The most common attack on these healthcare providers was ransomware. Due to the confidential and sensitive information hospitals and other health providers keep, ransomware is the most effective method for cybercriminals to extort money from their victims.
Ransomware is a cyberattack in which hackers take control of their target's files, data, or devices. They will then demand a ransom payment to return the target’s assets and confidentiality.
Ransomware is growing rapidly, increasing from 46 to 56 incidents from 2021 - 2022, and has continued to grow throughout the first half of 2023.
How Does Ransomware Work?
The most common form of ransomware is “encryption ransomware,” which happens when the victim’s network becomes infected via malicious email attachments, downloads, fake websites, or software vulnerabilities.
Once installed, the ransomware encrypts files on the local hard drive, rendering them inaccessible and unreadable. To regain access, the attacker demands a ransom payment, often in Bitcoin, in exchange for a decryption key that returns the files to their original state.
Other Common Types of Data Breaches to the Healthcare Industry
Data-related threats are the healthcare industry's most significant concern and are classified as either data breaches or leaks.
A data breach is an intentional attack by a cybercriminal aiming to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. A data leak, on the other hand, is the unintentional release of confidential information, such as human error or poor security practices.
Aside from ransomware, the following are other common threats to the healthcare industry.

Distributed Denial of Service Attacks (DDoS)
A Distributed Denial of Service Attack uses bots to flood a website or online service to the point where they overload the website’s server. This attack aims to slow the website down or make it inaccessible. A DDoS attack on a hospital disrupts communication between staff and patients and hinders access to patient data.
In early 2023, the rise of pro-Russian hacktivism increased the number of DDoS attacks across Europe, with a total of 20 incidents on European health authorities across the Netherlands, Denmark, Sweden, and Spain.
Malware
Malware, short for malicious software, refers to software designed to harm, exploit, or compromise computer systems, networks, devices, and data.
In the health sector, 5% of incidents involved malware. In these cases, phishing emails were infected with malware and sent to customers and patients to trick them into clicking on an infected link or file that would then steal their sensitive data.
Social Engineering, Intrusion, and Other Cybersecurity Threats to The Healthcare Industry
As the healthcare sector relies on maintaining and storing sensitive data, it is a prime target for cybercriminals searching for huge profits. Because of this, ransomware and data-related threats were reported as the most common attacks. Nevertheless, organizations are also at risk from a broader range of attacks, as shown below.
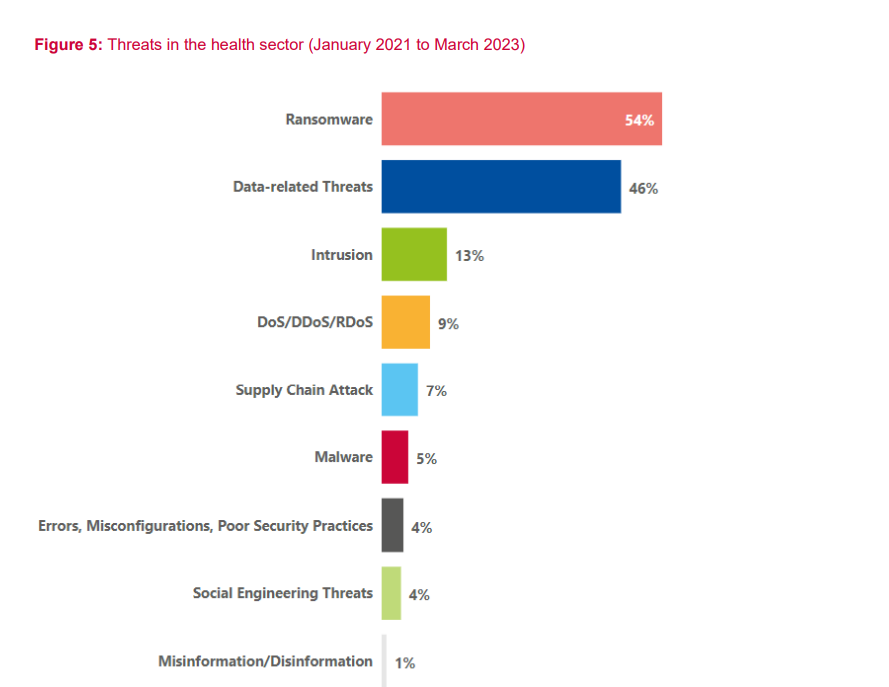
Data Breaches in the Healthcare Sector, 2023
The following three incidents of data breaches in 2023 exemplify how devastating a cyberattack can be to health organizations, both for the company and its victims.
Two of these attacks were carried out by the infamous hacker groups Ransom House and LockBit, the latter being responsible for the most incidents compared to these groups reported below.
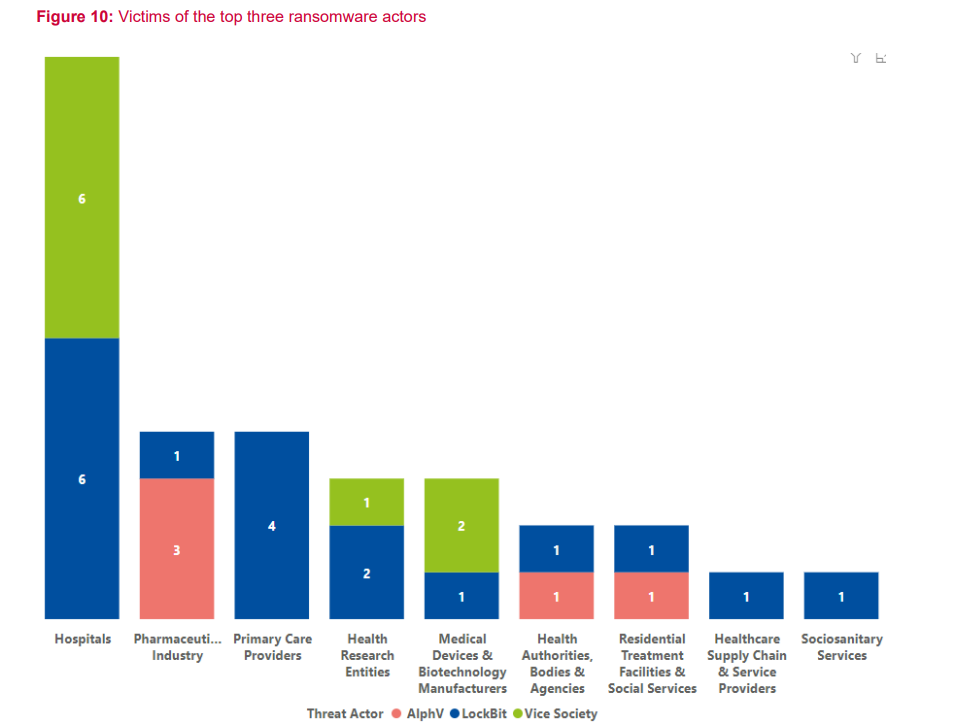
Let’s take a look at three of the most significant data breach attacks of 2023, starting with the USA.
The Managed North Care of America (MCNA)
The MCNA provides dental insurance to private employers, individuals, and families in the United States. It is one of the US's largest government-sponsored dental and oral healthcare providers.
On March 6, 2023, the MCNA said they were made aware of unauthorized computer access. Once an investigation occurred, it was discovered that the attack happened on February 26. Shortly after, a notification was issued to the office of the Maine Attorney General, stating that 8,923,662 people were affected by the breach.
LockBit claimed responsibility for the attack on March 7 and threatened to release 700GB of sensitive information unless the MCNA paid a $10 million ransom before April 6.
On April 7, LockBit released the stolen data, making the following available to the public for download.
- Full names, addresses, phone numbers
- Social Security and government numbers
- Health insurance plans
- X-rays, medicines prescriptions, dentist name, and treatment
Given that the leaked information is likely to be downloaded by other cybercriminals, anyone associated with the MNCA at that time must regularly monitor their credit activity to protect themselves against identity theft or fraud.
Hospital Clínic De Barcelona
On March 5, 2023, the Hospital Clínic in Barcelona suffered a ransomware attack by the cybercriminal group Ransom House. The Hospital’s IT and cybersecurity service quickly alerted the Catalan Cybersecurity Agency to find out what kinds of data were stolen and what solutions were available.
Ransomware was introduced because of the hospital’s outdated software, a common vulnerability hackers expose. This vulnerability caused an unauthorized intrusion of hospital software and the subsequent theft and encryption of its data.
As a result of this attack, 4.5 terabytes of personal data was compromised. For its return, Ransom House demanded a payment of $4.5 million to keep this data from becoming available to download by the public.
The data stolen from the attack was subsequently published for sale on the dark web after the hospital refused to pay, making the following sensitive information of patients available for purchase.
- Admission and medical records
- Medical orders
- Operating theatre reports
- Race, sexual orientation, and religious beliefs
This attack also seriously affected how the hospital handled patient care and administration. Nurses had to deal with patient cases on paper manually, and ambulances had to be diverted to other hospitals across Barcelona. Furthermore, the hospital had to cancel 150 non-urgent operations and 3,000 appointments.

Centre Hospitalier Universitaire (CHU) Saint-Pierre, Belgium
From March 10 to 11, a university hospital in Brussels became another cyberattack victim. The hospital's CEO, Pierre Leroy, said the hospital became aware of the attack after “Our specialists were able to detect abnormal activity on the computer network.”
Fortunately, the hospital implemented an emergency plan involving the staff to switch to working with paper records, and all ambulances were diverted to neighboring hospitals as a precaution.
The hospital also disconnected its servers to prevent damage to the system, and hospital officials stated that there was no indication of any personal or sensitive data being compromised because of the attack.
How Can Hospitals Prevent Data Breaches in Healthcare?
For healthcare professionals, it is crucial to be aware of the risks of cyberattacks within the industry. In a study by the ENISA, only 27% of industries in the health sector have a dedicated ransomware defense system.
Cybersecurity knowledge must be passed on to non-IT professionals, as anyone working with sensitive information or who works online should increase their cyber awareness. The same study by the ENISA showed that 40% of non-IT staff have no awareness or training of cybersecurity risks.
To protect hospitals, patients, and staff, healthcare providers should follow cyber hygiene practices that can help mitigate cyberattack threats. Implementing cloud-based practice management systems can further enhance security and streamline operations
Cloud Storage Integration
Cloud storage solutions are rapidly becoming the norm not only for individuals but for large-scale businesses, too. A secure cloud storage provider will implement security measures, and follow compliance laws that protects medical data like the GDPR or HIPAA.
One of the most effective means cloud storage can help protect against cyberattacks is backups. Using cloud backups to protect against ransomware means even if files are encyypted on one device, the backed up files are still accessible from another device in the cloud.
One of the most effective means cloud storage can help protect against cyberattacks is backups. Using cloud backups to protect against ransomware means even if files are encyypted on one device, the backed up files are still accessible from another device in the cloud.
Internxt Drive offers cloud storage backup solutions to help protect sensitive data from ransomware, protected by zero-knowledge and end-to-end encryption for maximum security.
With secure cloud storage, hospitals or other health organizations can encrypt the data they store at rest and in transit, meaning the data is encrypted when stored in the cloud and when data is being transferred, keeping it secure against external parties or hackers.
Cloud storage providers are also responsible for maintaining the security of their platforms. They will continually update and patch their systems for security threats, reducing the number of attacks on hospitals caused by outdated software, as was the case with the Hospital Clinic De Barcelona.
Employee Training and Awareness
16% of attacks are caused by human error, which can be avoided if organizations train employees to recognize the signs of common cyber threats, such as phishing emails.
Therefore, employees should be trained on the features of HIPAA compliance to understand and prevent cybersecurity attacks. Employees should also know how to recognize and report suspicious phishing emails, as this is a common way for cybercriminals to introduce ransomware into the system.
Other cyber hygiene tips employees can follow are:
- Password Management: Teach employees the essentials of a strong password (long, complex, and unique) and how to integrate their password with multi-factor authentication.
- Software Updates: Employees should keep their devices, mobiles, tablets, and computers updated at all times to reduce the risk of malware being introduced to outdated software.
- Regular Training Updates: Training and staying updated with security issues will help employees identify and report suspicious activity before too much damage is done.
Conduct Regular Cybersecurity Assessments and Training
Cybersecurity assessments should assess risks in the organization’s IT systems, networks, and applications to identify or address potential vulnerabilities, weaknesses, or areas for improvement.
The goal of these assessments is to gain an understanding of the organization’s strengths and weaknesses. One way to do this is by conducting penetration testing (pen testing), which is the process of:
- Planning: Define the objectives and methods of testing in the organization
- Reconnaissance: Gathering information about the infrastructure and systems that can be targeted for attack
- Exploitation: Attempt to exploit these vulnerabilities to gain access to the platform for malicious intentions
- Reporting: Document the findings, the methods used, and the potential impacts if the issues are not addressed
- Remedy: Provide recommendations to fix the vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
Regular assessments and tests conducted by the right people can significantly help hospitals and related healthcare organizations take corrective actions before they become prime targets for cybercriminals.
Investing in cybersecurity for healthcare will promote a culture of awareness that will ensure the well-being of the hospital, its employees, and its patients.
Furthermore, a data breach report by IBM shows healthcare has consistently ranked the highest for data breach costs, at $10.93 million. The financial industry came in second, at $5.9 million, and pharmaceuticals managed to lower their data breach costs from $5.01 in 2022 to $4.82 million in 2023.

The Future of Healthcare Security for Patients and Health Professionals
With attacks on healthcare industries continuing to break records every year, hospitals and other healthcare organizations must comply with privacy laws laid out by governments to defend against the constant threats of attacks on data.
As the future of healthcare continues to develop innovative technologies, the risk of security incidents for hospitals will never disappear. As a result, the healthcare industry needs to be prepared for a future based on protecting its patients' lives and data.

