The History of Cybersecurity: Key Moments in Technology and Privacy

The History of Cybersecurity: Key Moments in Technology and Privacy
For Cybersecurity Awareness Month, we are taking a look at the past, present, and future and looking at key moments from the history of cybersecurity.
Because of our past technology, we are able to explore limitless possibillities with technology that shapes how we work, communicate, and consume media. We will also look at how
1940’s to 60’s: The begininngs of cybersecurity
Let’s start from the very beginning with the very first developments in technology and cryptography that influenced programming, file storage, and password security.
1943: Colossus

Tommy Flowers and British codebreakers developed the first set of programmable, electronic set of computers, Colossus, between 1943 and 1945. Colossus was designed to help British forces analyze the Lorenz Cipher to intercept and decode German communications during WWII.
Colossus was successful in providing the British with the resources and intelligence needed to analyze the German forces, which in turn helped shorten the war and save hundreds of thousands of lives.
1957: Fortran
IBM, led by John Backus, developed the first high-level programming language Fortran, (Formula Transition). It was the first high-level language designed for science and engineering purposes to solve complex differential equations for fields like physics, engineering, meteorology, and astronomy.
Thanks to Fortran, we can thank him for software languages such as ALGOL, BASIC, C, MATLAB, and Python, making it one of the most significant contributions in the history of cybersecurity.
1961: Compatible Time-Sharing System (CTSS)
In 1961, MIT developed the Compatible Time-Sharing System (CTSS), allowing multiple users to work simultaneously on a computer by dividing processing time so users could write and run programs, edit files, and communicate in a shared environment for the first time in history.
CTTS's pioneered key concepts that are foundational in modern computing. For example, CTTS is a precursor to modern multi-user operating systems, which later evolved into cloud computing and virtual machines, allowing multiple users to share computing resources over a network.
1970’s to 90’s
Now that the foundations are set for technology, the mid-point of the history of cybersecurity saw the developments of the internet, virus, and anti-virus software.
1971: Creeper
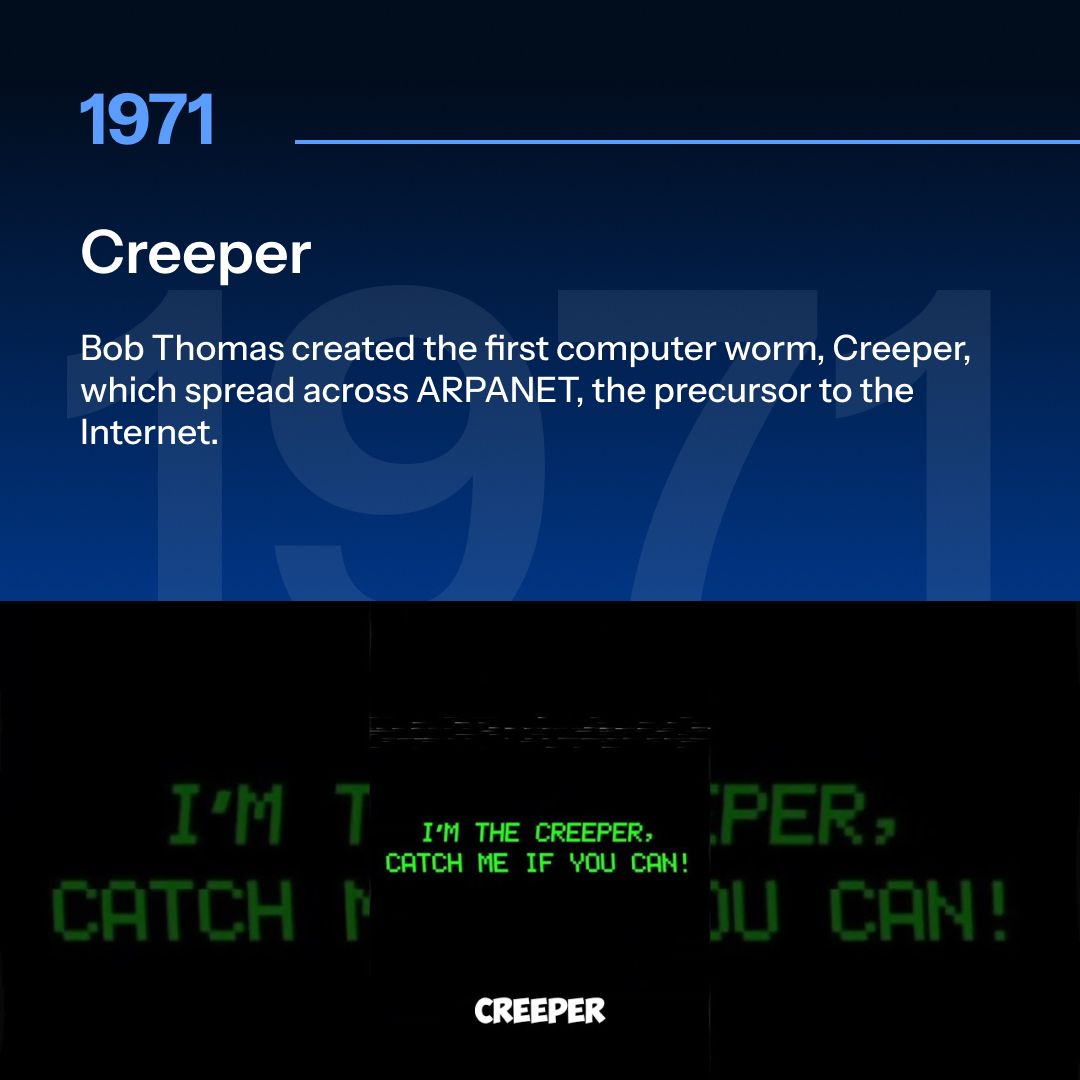
In 1971, Bob Thomas of BBN Technologies designed a self-replicating program known as The Creeper Worm. The Creeper was designed as a test to demonstrate the concept of self-replicating software and not to cause damage by displaying the message:
"I'M THE CREEPER : CATCH ME IF YOU CAN"
This message spread across 28 machines, but no files were corrupted, changed, or deleted.
The Creeper worm meant researchers could study the behavior of network systems and the potential for self-replicating programs. One year later, Ray Tomlinson developed the first anti-virus, The Reaper, to delete the worm.
1989: World Wide Web
Another major milestone in the history of cybersecurity was Tim Berners-Lee's invention of the World Wide Web in 1989, which allowed researchers to access and link documents across different systems easily.
Alongside accessing and linking documents, the first web browser and HTML (HyperText Markup Language) let users navigate between pages with hyperlinks. This invention formed the foundation of what we now know as the Internet, which we all use for messaging shopping, education, streaming, and storage.
1999: The Melissa Virus
In 1999, David L. Smith created one of the first widespread email viruses. Once the virus was opened via an infected Word document, it spread to the first 50 contacts in the user’s email address book.
The virus caused significant disruptions to email servers across the globe, although it cause widespread slowdowns due to overwhelming email traffic it caused, demonstrating how quickly malware could spread via email.
2000’s, 2010’s, 2020’s
Past the Y2K scare, technology continued to develop rapidly, becoming more accessible to households worldwide. To keep up with these developments, cybersecurity experts and businesses had to take quick, practical measures to protect confidential information and customer data.
2013: Edward Snowden Revelations

2013 was a major year for how the public viewed privacy, security, and government surveillance.
Edward Snowden is a former NSA contractor who exposed widespread global surveillance programs run by the National Security Agency and its international partners. The leaked documents exposed how these organizations collected data on the public’s phone calls, emails, and internet activity of citizens worldwide.
The Edward Snowden revelations in 2013 exposed widespread global surveillance programs run by the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) and its international partners.
Snowden, a former NSA contractor, leaked classified documents that revealed the extent of data collection on phone calls, emails, and internet activity, not just of suspected criminals but also of ordinary citizens worldwide. His disclosures sparked intense public debate about privacy, security, and government overreach.
The significance of the Snowden revelations lies in the global shift in data privacy policies. In response, several countries introduced or strengthened privacy laws, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and stronger encryption methods.
2023: AI and ML

AI and machine learning gained popularity due to advancements in computational power, the availability of vast amounts of data, and significant improvements in algorithms.
The proliferation of smartphones, IoT devices, and digital services has generated immense data, enabling machine learning models to learn and improve from real-world inputs.
2030s and beyond
So, what does the future hold for cybersecurity?
Quantum Cryptography

Quantum cryptography will be one of the most crucial technology that will protect our cloud storage, financial transactions, and all confidential information for businesses.
Duie to the power of quantum computers, they could theoretically break the encryption of today’s conventional encryption, exposing all our files.
Therefore, post-quantum encryption is being developed to prevent the threats of quantum computers and keep us working online with total security and privacy.
What does the future of cybersecurity hold?
The future of cybersecurity may be filled with more threats and breaches to our data, but with the right security measures and care towards our online privacy, we can all help protect our online presence.

For threats such as quantum computers breaking traditional encryption technology, Internxt is preparing to protect your data in the cloud by implementing post-quantum encryption tech to ensure your data remains protected.
Subscribe to Internxt Drive today to secure your future online!

