Is Zero Trust Widely Accepted?

Cyber threats are evolving and are one of the reasons why data breach costs increase each year, and traditional security models are struggling to keep up. As businesses embrace cloud computing and working remotely, the old "trust but verify" approach is proving inadequate, leading to the increased adoption of zero-trust policies.
But is Zero Trust widely accepted? The answer is increasingly yes.
So, how does Zero Trust work, and what makes it so effective? In this article, we’ll explore its key components, benefits, challenges, and how to set up your company for success and security with the help of Internxt Drive.
Table of contents
- Identity and access management
- Device security
- Least privilege
- Network segmentation
- Monitoring and analytics
- Encryption and data protection
- Identify and classify assets
- Authentication for third-parties
- Micro access controls
- Secure data with cloud storage
Introduction to zero trust
When considering is zero trust widely accepted in various industries, some may think that it’s just another security buzzword. Instead, it’s a necessary shift in how organizations protect their data with remote access security.
Zero trust marks a shift in how businesses operate with a strict never trust, always verify principle. As a result, companies have extra security by ensuring every user, device, and application is verified before accessing sensitive information.
For example, an employee working remotely in a traditional security model would log in to a company's database and, once accepted, they may have unrestricted access to various systems that don’t require additional verification.
This poses a higher security risk because if their credentials were stolen or their device was compromised, anybody could move freely within the network, potentially causing significant damage to the company.
With Zero Trust, the employee wouldn’t automatically be trusted based on the initial login but would instead have to verify every access request at multiple levels.
Accepting a new zero-trust system means using multi-factor authentication at each level, which can be monitored by account managers and any suspicious activity can be checked and prevented to prevent lateral attacks by hackers or insider threats.
Why zero trust matters today
Zero trust matters today because of increased high-profile data breaches, regulatory pressures, and the rise of sophisticated cyberattacks, such as AI phishing and ransomware, which have forced companies to rethink their security protocols.
As a result, startups, Fortune 500 companies, and organizations across all industries are adopting Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) to reduce risk, improve compliance, and protect data.
The growth of remote work in 2024, with approximately 40% of companies globally, coupled with BYOD policies, has expanded the attack surface for businesses. Employees connecting to corporate systems from personal devices and unsecured networks have increased the risk of credential theft and malware infections.
With the correct security measures, companies can ensure that even if attackers steal credentials, they cannot move freely within the network without further authentication and authorization checks.
Key components of zero trust
If you’re one of the companies asking is zero-trust widely accepted, then you will also need to know what are the key components of a zero-trust architecture (ZTA). Below, you will find how zero trust is implemented within organizations.
Identity and access management
The main feature of ZTA is identity and access management- This is the foundation of this kind of security policy and ensures that only authenticated and authorized users can access resources.
It uses multi-factor authentication (MFA), single sign-on (SSO), and strict role-based access control (RBAC) to verify users before granting them permissions and access to potentially sensitive information. Before allowing access, other authentication techniques can analyze user behavior and risk factors, such as login location and device security posture.
Device security
To increase the security of bring your own device policies, device security assesses the trustworthiness of any device connecting to the network. Unmanaged or non-compliant devices can be restricted or blocked to prevent security risks.

For example, a company should require employees to register their laptops and smartphones with the organization's mobile device management (MDM) system. Before allowing access to corporate applications, the MDM solution checks whether the device has up-to-date security patches, antivirus software, and encryption enabled.
Least privilege
Least privilege access only gives users and systems the minimum permissions necessary to perform their tasks. Implementing least privilege means access is granted on a need-to-know basis, reducing the attack surface and limiting the damage should anyone try to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Network segmentation
Network segmentation breaks your network into smaller, isolated segments to prevent attackers from moving laterally across systems. Micro-segmentation enforces strict access policies between different applications, devices, or user groups, ensuring that attackers cannot freely access the rest of the network even if one segment is compromised.
Monitoring and analytics
Zero trust is becoming more widely accepted thanks to the development of technology, specifically with monitoring and analytics tools that can automate monitoring and verifying user activity.
Security information and event management (SIEM) tools, user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA), and AI-driven threat detection help identify anomalies and potential security threats.
By blocking access or requiring additional authentication, suspicious activity can be detected quicker, and your team can take action and eliminate potential threats.
Encryption and data protection
Encryption and data protection secure sensitive information both in transit and at rest. Zero-knowledge encryption, like with Internxt, also ensures increased privacy, as the encryption keys are stored on your device, meaning nobody else, not even the cloud provider, can access them.

How to Implement Zero Trust in Your Organization
Identify and classify assets
To get started with a zero-trust system, your team should identify all assets within your organization, including users, devices, applications, and data.
You should also catalog all employees’ roles and responsibilities, including their devices and any sensitive data (customer information, financial records) they can access.
If you work in healthcare, for example, you can classify patient data as highly sensitive and restrict access to only specific departments or individuals, while general administrative data might be more broadly available but still monitored.
Authentication for third-parties
If your company works with external partners or services, you can issue short-lived, one-time access tokens that provide limited access to sensitive data. This ensures third parties are never given permanent access to sensitive information, significantly reducing the chances of a security breach from third-parties.
Micro access controls
Prevent blanket access to information by enforcing micro access controls, which restrict user access to resources that are only necessary to their roles.
For instance, an HR employee could only access specific payroll files for their department during working hours. Access is denied if they attempt to access files from another department or outside designated hours, and additional authentication is required.
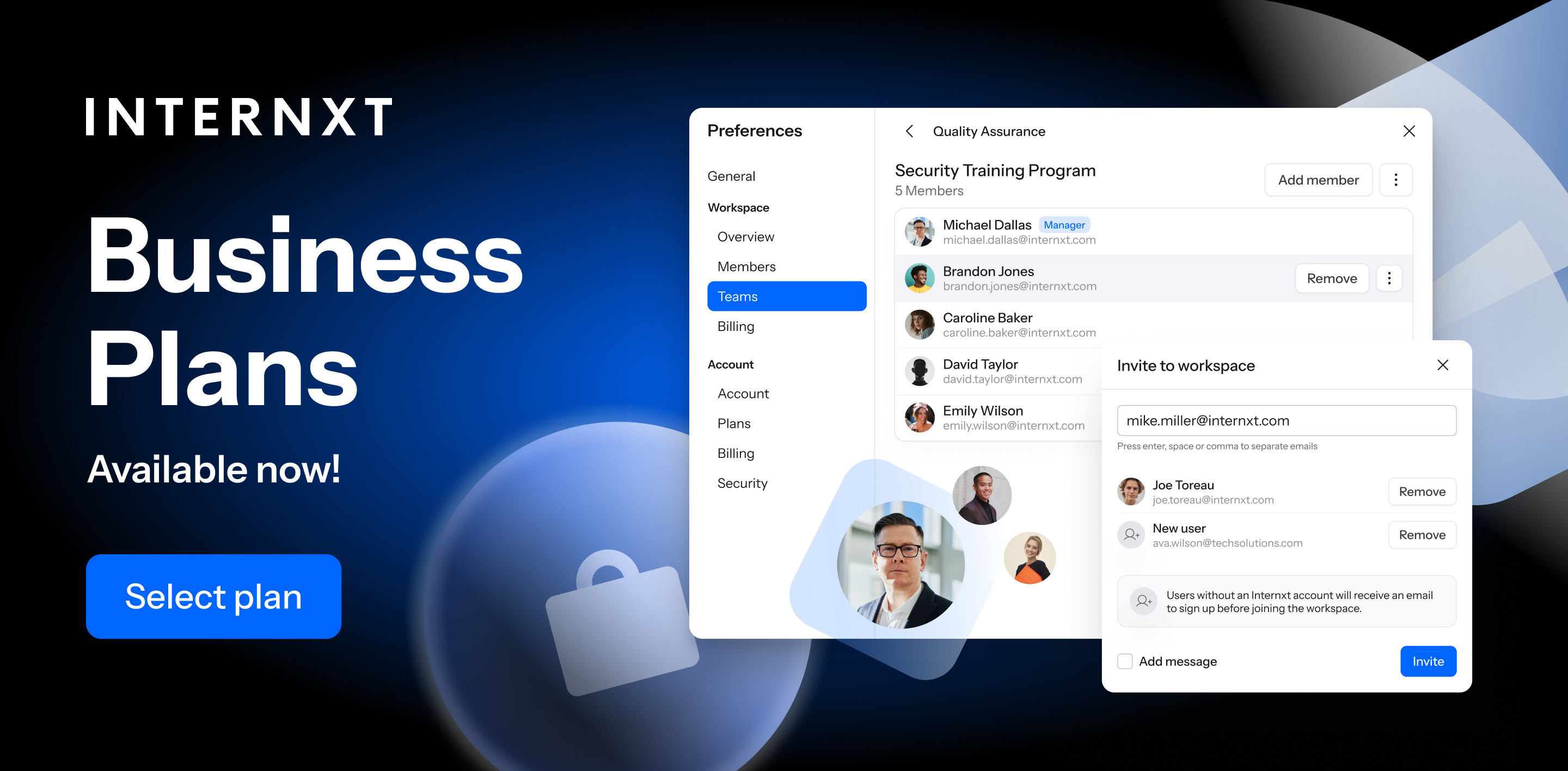
Secure data with cloud storage
Is zero trust widely accepted in cloud storage? With Internxt, yes, it offers many security features to to keep business data protected and private in the cloud.
Internxt Cloud Storage for Business is GDPR compliant cloud provider that ensures data privacy and legal compliance, potentially saving businesses millions as it helps prevent data breaches and compliance fines.
With zero-knowledge encryption, Internxt ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive information, protecting data from unauthorized access. It provides scalable and secure storage for companies with up to 100 users.
As the first company with post-quantum encryption, Internxt ensures long-term data protection against emerging threats of quantum computers, which could break current encryption technology.
Internxt Drive also offers increased control for account managers, with features such as access logs and account monitoring, allowing businesses to track user activities and detect potential risks, reinforcing a zero-trust approach to security.
Internxt also offers S3-compatible, which offers the same security for businesses needing a large data storage platform at just €7/TB/month.

To get started with Internxt Drive for your business, visit our website to contact our sales team.
Is zero trust widely accepted for the future?
As we can see, zero trust is increasingly being recognized as a critical security model for the future, particularly as cyber threats evolve, quantum computing becomes more common, and other potential threats from hackers.
To start your journey to a more secure future, consider using Internxt Cloud Storage for your business. With its GDPR compliance, zero-knowledge encryption, and innovative post-quantum encryption, Internxt offers a private and secure solution to protect your company’s data and build a secure security policy for your business and team.

